Complex search
Dynamic placeholders
The following placeholders can be used anywhere in the monitor in filters/searches. These are replaced accordingly during the query of the data.
| Placeholder | Example replacement | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
max.mustermann |
Login name of the current user. |
Full text search in the monitor
The full text search provides the central search functionality across all fields of the currently selected monitor. You can not only enter individual search terms in the input field, but also compile complex searches using operators.
A window for the full-text search is available to the user in the information and function area. The full-text search is carried out across all monitoring data. It works across all columns and can optionally be preset to include all process details and referenced messages.
To find data, the user enters the search term in the full-text search field in the function bar. Multiple search terms can be linked together using operators.
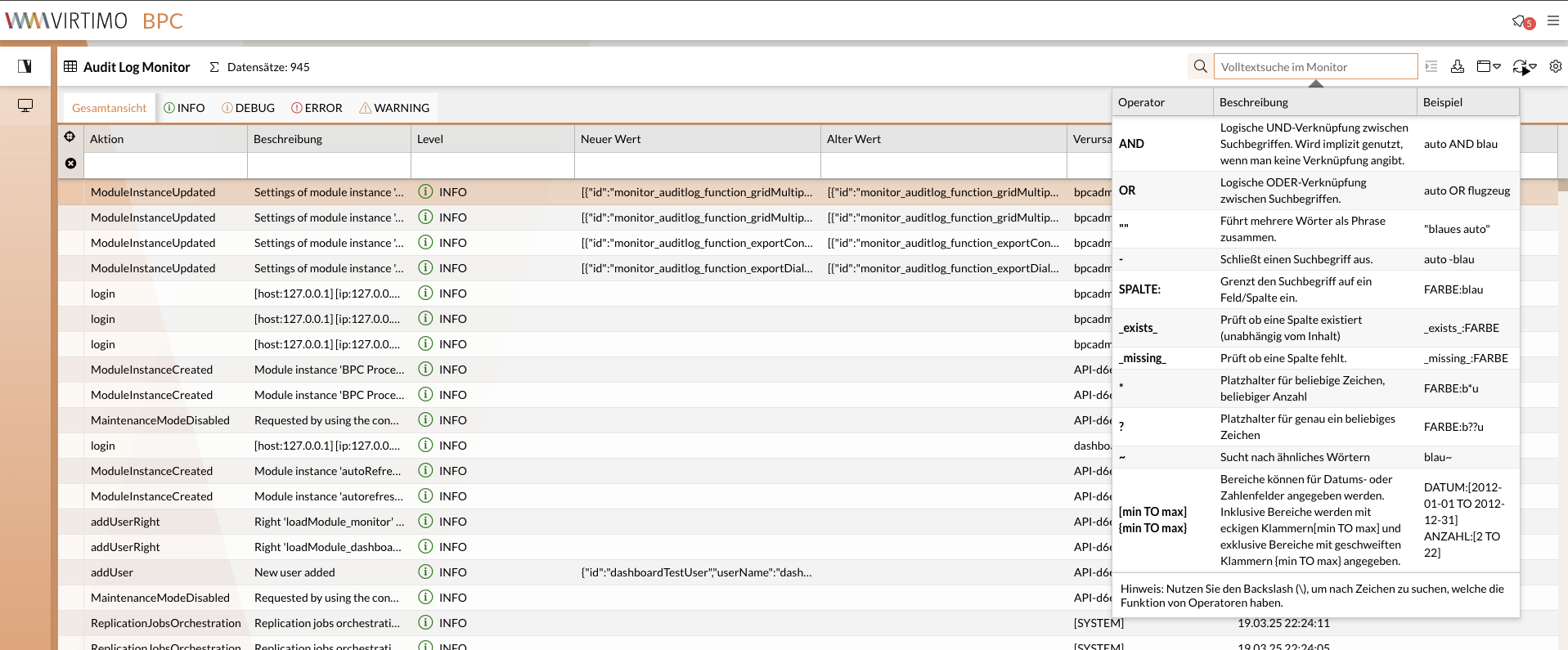
If no operator is specified, the terms are linked with AND.
Linking search terms
If no quotation marks (") are used, the space separates two words syntactically and considers them separately.
In this case, the logical AND (AND) is used as the linking operator.
If you want to link with the logical OR, you must explicitly specify OR.
| Example | Explanation |
|---|---|
|
Searches for documents that contain "auto" in any field and "blue" in a (possibly different field). |
|
Searches for documents that contain "auto" or "blue" in any field. |
|
Parentheses can be used for more complex logical links. |
Limiting the search area
If you want to limit the search to a specific field, you can do this by separating the field name (column name) with a colon.
| Example | Explanation |
|---|---|
|
Searches for documents in which the value "auto" appears in the VEHICLE TYPE field and the value "blue" in the COLOR field. |
Exclude search terms
You can also negate/exclude the search or parts of the search.
| Example | Explanation |
|---|---|
|
Searches for documents in which the value "auto" occurs in the VEHICLE TYPE field and the value "blue" does not occur in the COLOUR field. |
Search for (non-)existing fields
If you want to find documents in which certain fields exist or are explicitly missing, you can work with the keywords _missing_ and _exists_.
| Example | Explanation |
|---|---|
|
Searches for documents with the field KAEUFER, regardless of content, without the field SONDERAUSSTATTUNG. |
Wildcard/placeholder search
Placeholders (wildcards) can also be used for fields that contain text. There are two different wildcards.
The ? stands for any character (only one character) and * stands for an unspecified number of any characters.
| Example | Explanation |
|---|---|
|
Searches for colors beginning with "gr", such as "green" and "gray" and "gray-blue". |
|
This search would also find "green" and "gray", but not "gray-blue". |
Search for similar words / fuzzy search
For fields with text, it is possible to search for "similar" words. This can be used to find words containing typing errors, for example.
| Example | Explanation |
|---|---|
|
Also finds the color "blua". |
|
Changes the distance after the operator. |
Range search
Intervals can be specified for date or number fields.
Inclusive intervals (which include the limits) are specified with square brackets [min TO max] and exclusive intervals (which do not include the limits) with curly brackets {min TO max}.
Curly and square brackets can be combined.
Alternatively, the operators <, >, <= and >= can also be used if there is a restriction from one side only.
| Example | Explanation |
|---|---|
|
All days in 2012 |
|
Numbers 1 to 5 |
|
Numbers from 10 upwards |
|
Dates before 2012 |
|
Numbers from 1 to 4 |
|
Areas with a page without a limit |
Special characters in the search term
If the search term contains special characters that normally represent an operator for the search, these must be masked (escaped) with \.
This masked text is then not treated as an operator, but as normal text.
| Example | Explanation |
|---|---|
|
Uses the entire sentence as a search term and hides |
Limitation for complex search queries
By default, the number of concatenated search terms in OpenSearch is limited to 1024.
A text search that does not refer to a specific field generates one search term per field internally.
For indices with many fields and several logical links (AND, OR), the limit of 1024 terms can therefore be reached quickly.
In this case, the error message appears: too_many_nested_clauses.
If this error occurs, the search query should be optimized by a targeted field search (column search).
If it is absolutely necessary to use more complex search queries, the limit can be adjusted in the configuration file OPENSEARCH_CONFIG_VERZEICHNIS/opensearch.yml by adding the following line:
indices.query.bool.max_clause_count: 2048The value (here 2048) can be adjusted as required. After the change, OpenSearch must be restarted.
|
Increasing this limit is not recommended, as very complex search queries can significantly impair system performance. |
Overview of search parameters/operators
| Operator | Function | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
merges several words as a phrase |
|
|
groups operators to link them with other searches via AND/OR |
|
|
signals a substring search with any number of variable characters |
|
|
signals a substring search with one variable character |
|
|
Fuzzy search |
|
|
Treats reserved operators as normal text. |
|
|
Boolean AND function |
|
|
Boolean OR function |
|
|
excludes phrase |
|
|
Column search |
|
|
Entries without value in column1 |
|
|
Entries with value in column1 |
|
|
Interval search with inclusive limits for number and date fields |
|
|
Interval search with exclusive limits for number and date fields |
|
|
Filter operators for numeric comparisons: less than, greater than, less than or equal to, greater than or equal to |
|
