OpenSearch indices view
Overview
The indices view in BPC provides a detailed overview of all existing indices. An index in OpenSearch is comparable to a database table and contains various metadata and configuration options. In this view, users can manage indices by:
-
Filter indices
-
Update indices (bring table up to date)
-
Manage indices:
-
Display the mapping and settings of an index
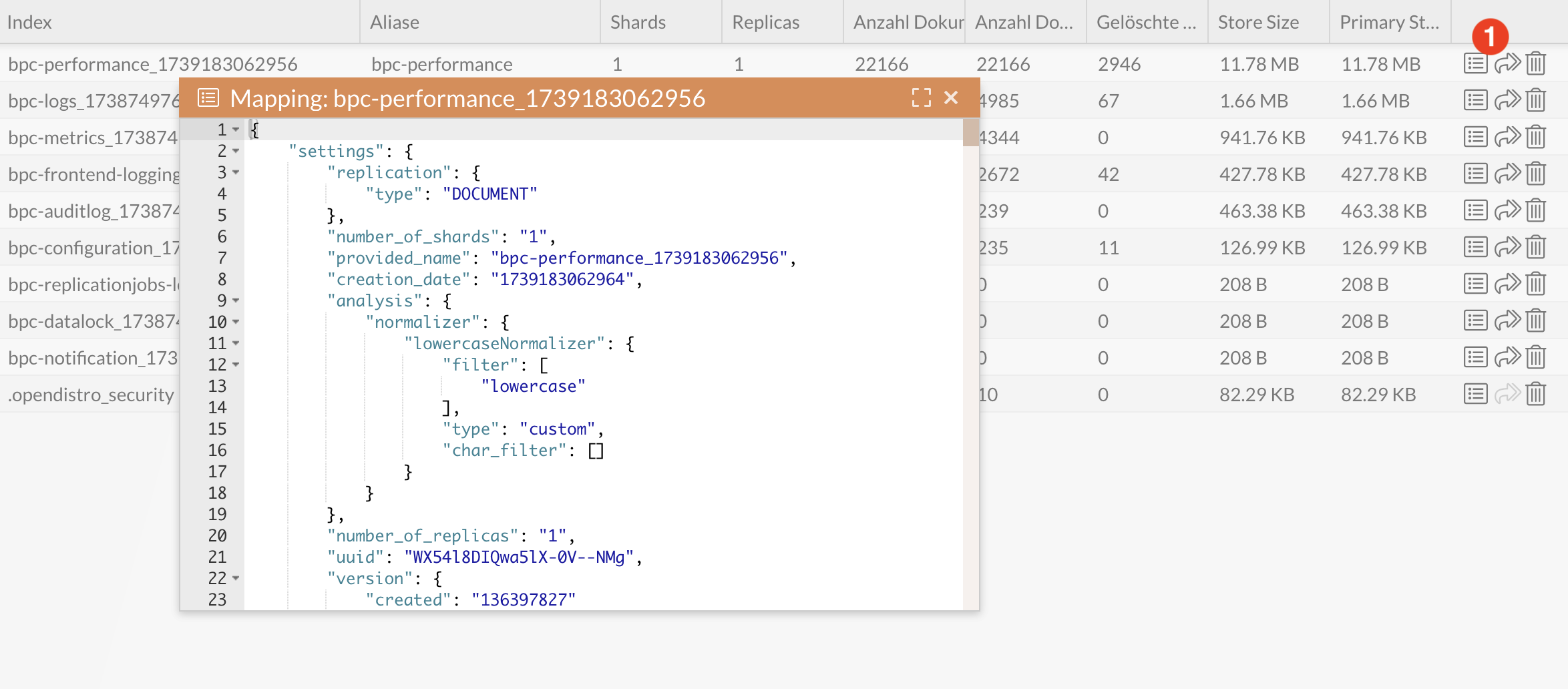
-
- Reindex indices
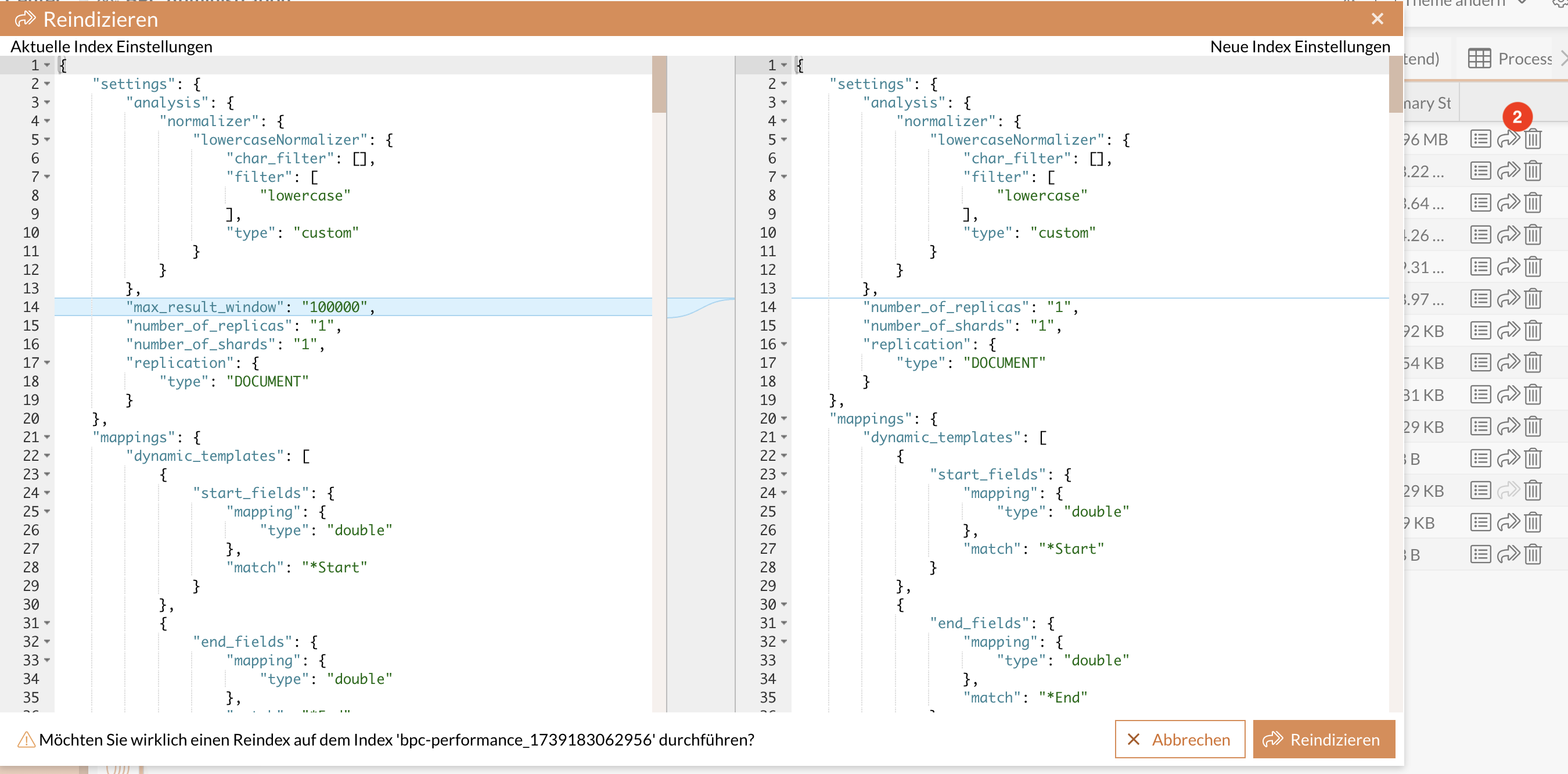
-
- Export indices as a ZIP file. (This can be used to install a preconfigured BPC.)
-
Delete indexes (Warning: leads to data loss!)
-
In addition, the view displays various status information, including the index status (open or closed), and allows a detailed analysis of the indexes.
|
A closed index (activated by default) is blocked for read and write operations and does not allow all operations that are available for open indexes. It is not possible to index or search for documents in a closed index. This means that closed indexes do not have to maintain internal data structures for indexing or searching documents, which results in a lower load on the cluster. |
Color codes
The health status of the cluster, based on the status of its primary and replicated shards. Possible statuses are:
| Color code | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
The green circle indicates that all shards are assigned |
|
The orange circle indicates that all primary shards are assigned, but one or more replica shards are not assigned. If a node in the cluster fails, some data may be temporarily unavailable until the node is repaired |
|
The red circle indicates that one or more primary shards are unassigned, making some data unavailable. This can occur briefly during cluster startup when the primary shards are still being assigned. |
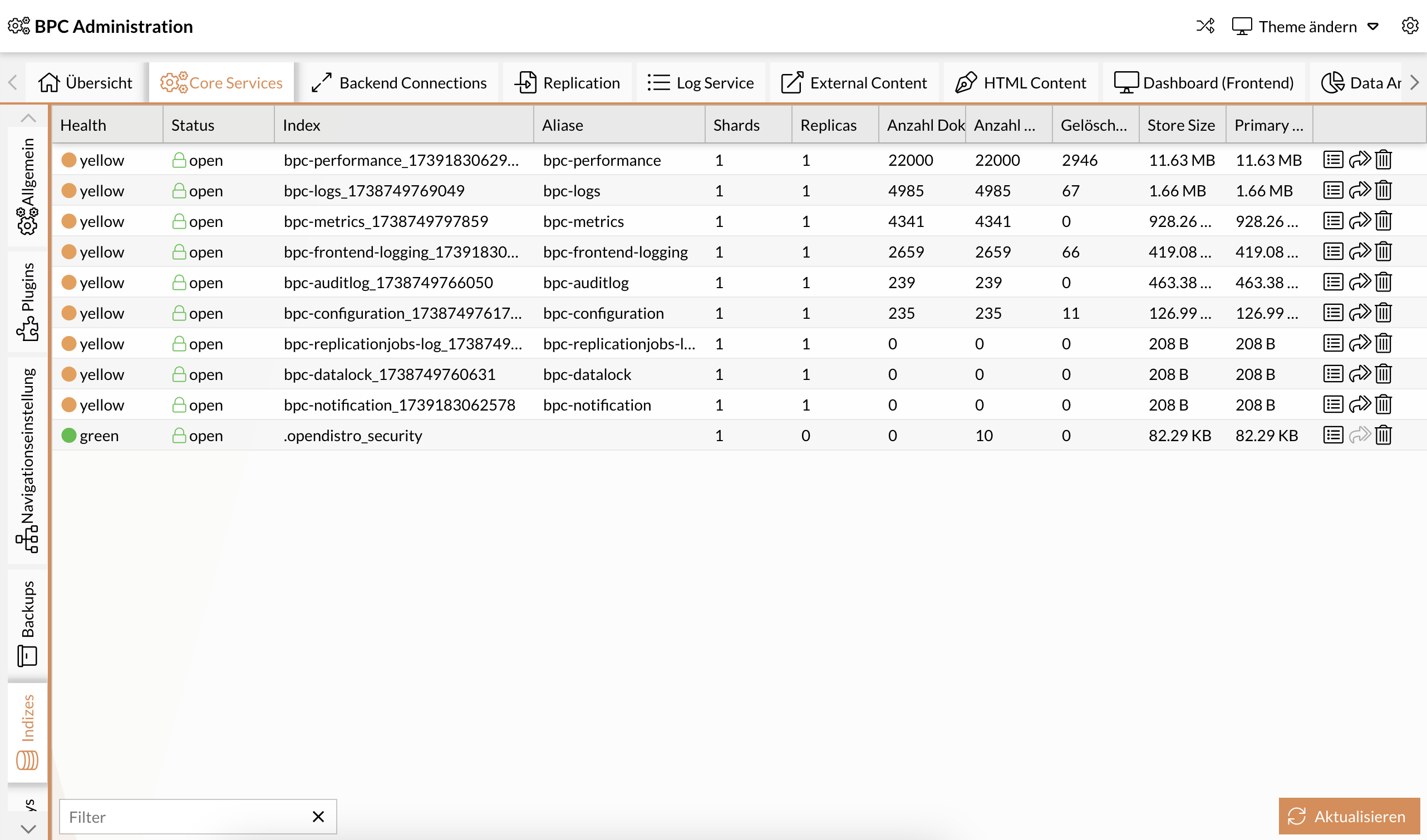
Columns in the indices view
-
Health: Shows the current state of the index (green, orange or red)
-
Status: Shows whether the index is set as "open" or "close"
-
Index: The name of the index
-
Aliases: Alias names that refer to the index
-
Shards: Number of shards of the index
-
Replicas: Number of replicas of an index
-
Number of documents: The total number of documents stored
-
Deleted documents: Number of documents marked as deleted
-
Store Size: Total storage space occupied by the index
-
Primary Store Size: Primary storage space
Overview of columns in the indexes view:
Indexes Management
Reindexing
Reindexing allows data to be transferred from an existing index to a new index.
Reasons for reindexing:
-
To remove documents marked as deleted, as these are not transferred to the new index.
-
To re-index the documents of the index with a possibly adjusted mapping.
When the Reindex feature is called up, the previous index settings and mappings are compared with those intended for the new index in the dialog that appears. The new index settings and mappings are set up as follows:
-
The mappings of the existing index are adopted.
-
If available, the mappings are transferred to the new index If available, the mappings for the new index are taken from one of the
managed_indices.jsonfiles. -
BPC Administration → Core Services → Allgemein → Core_IndexCreationSettings(indexCreationSettings)Example JSON configuration:{ "analysis": { "normalizer": { "lowercaseNormalizer": { "type": "custom", "char_filter": [], "filter": [ "lowercase" ] } } } } -
BPC Administration → Core Services → Allgemein → Core_IndexDynamicTemplates(indexDynamicTemplates)Beispiel JSON-Konfiguration:[ { "binaries": { "match_mapping_type": "string", "match": "_binary", "mapping": { "type": "binary" } } }, { "strings": { "match_mapping_type": "string", "match": "", "unmatch": "_binary", "path_unmatch": "bpc-attachment-.*", "mapping": { "type": "text", "fields": { "raw": { "type": "keyword" }, "lowercase": { "type": "keyword", "normalizer": "lowercaseNormalizer" } } } } } ]Depending on whether the index is filled by replication or a Log Service, there are various customization options:
Replication:
Up to three customization options can be used here for each replication job to influence the index settings and the mapping:
-
targetIndexCreationSettings = Index Settings (optional): If set, the global indexCreationSettings (see above) are not used.
-
targetIndexMappings = Index Mappings (optional): Specific mappings can be defined here if the automatic recognition of OpenSearch is insufficient.
-
targetIndexDynamicTemplates = Dynamic Templates (optional): If set, the global indexDynamicTemplates (see above) are not used.
Log Service:
For these indices, the mapping is created based on the fields configuration there. For more details, see the field naming convention in the Log Service.
Shards and replicas
Shards and replicas are central concepts for the distribution and security of data in OpenSearch (see also Shards and replicas of indices in OpenSearch).
Replica
Replicas are backup copies of shards that ensure data integrity in the event of a node failure.
The number of replicas can be set to 0, which is only useful for single-node or development systems.
In an OpenSearch cluster with at least two nodes, this value should be set to at least 1 to ensure reliability.
Shard
A shard contains the documents of an index and influences the performance and scalability:
-
An index can consist of one or more shards.
-
A single shard can store up to approx. 50 GB of data and approx. 200 million documents.
-
Large shards can slow down search queries and prolong recovery from errors.
-
Each shard requires heap memory and uses its own thread.
Backups
Regular backups of the indices are created to ensure data integrity. These enable recovery in the event of data loss or system failures.
