Plugins
It is possible to embed functions of individual modules in other modules using the plugin mechanism. A module that can be extended by plugins defines certain areas (called "hooks") in its interface in which plugins can be placed. A module that wants to offer plugin functions defines explicit plugin components (called "plugin").
Plugin is an element for the user interface. Each BPC module can provide plugins.
Hook is a type of placeholder that can be filled with one or more plugins. A BPC module can provide any number of these hooks.
Configuration
The specific assignment between hook and plugin is carried out by the administrator in the configuration area of the BPC. The tab of the module to which a plugin is to be assigned is first selected there. On the left-hand side, there is the "Plugins" item (this is only visible if the module in question is plugin-enabled).
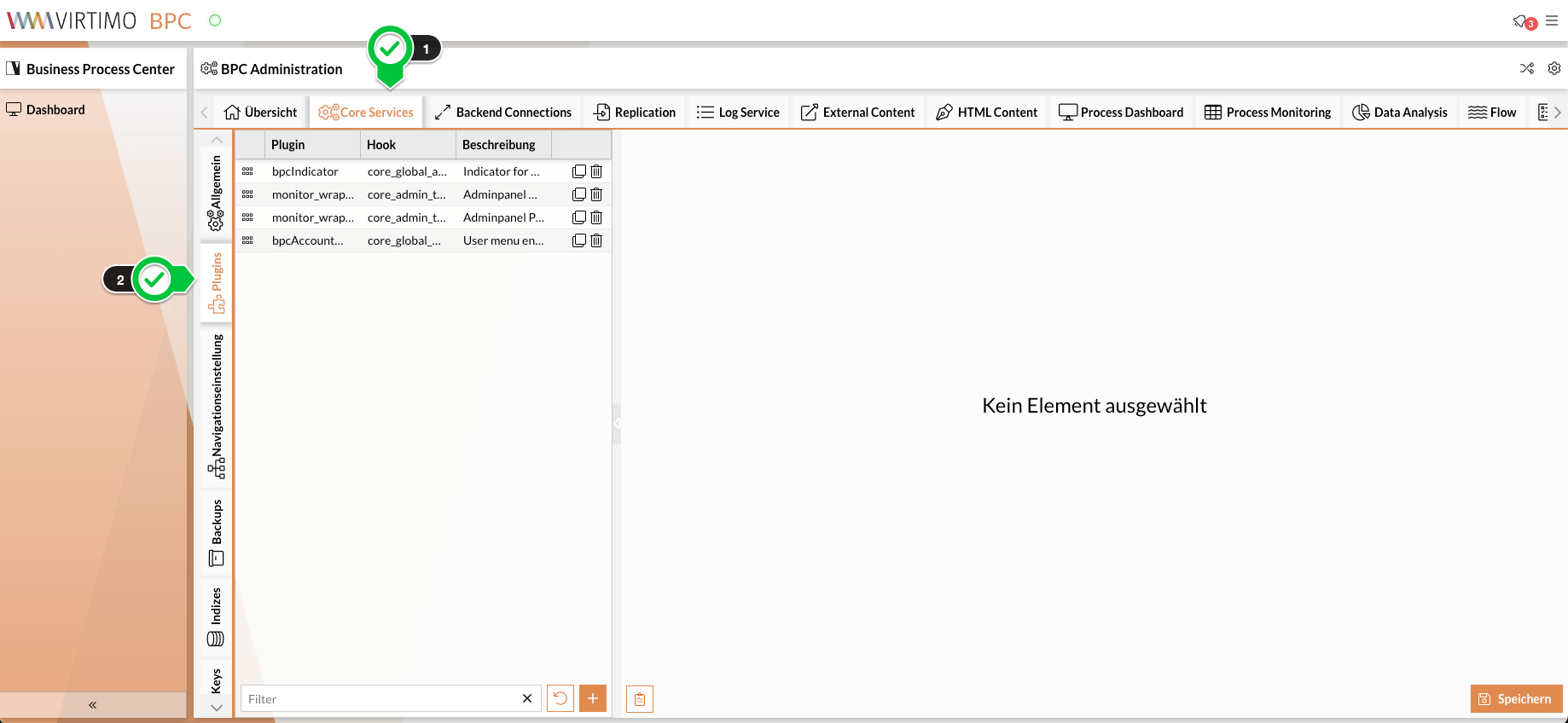
Plugins can be assigned to the module in the configuration interface. A new entry must be created in the list for this. The plugin to be used and the hook in which the plugin is to be placed are then selected on the left-hand side. The selected plugin can now be configured as follows:
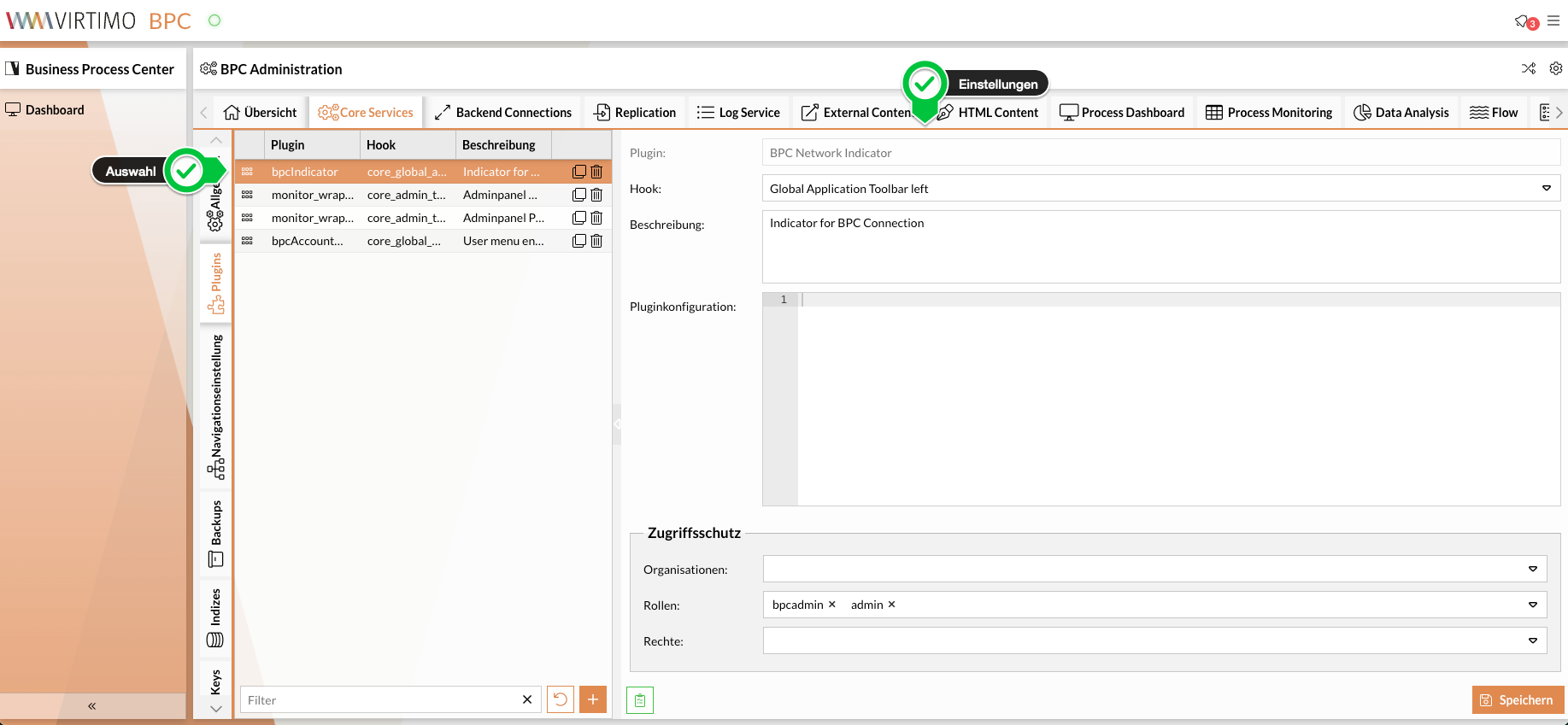
Plugin
Select a plugin. The list of available plugins depends on the modules that have been loaded by the BPC.
Hook
Hook in which the module is to be placed. The available hooks depend on the module in which the plugin configuration is currently being carried out.
Component
If the current module can consist of several components/instances (e.g. Process Monitoring), then a description can be entered.E.g. Process Monitoring), you can select here for which components/instances the plugin assignment should be taken into account. If nothing is entered here, the plugin is added to all components/instances.
Organization / Roles / Rights
Here you can make the plugin assignment dependent on the respective user. The plugin is only displayed if the user has the configured organization / roles / rights.
Plugin configuration
An additional JSON configuration can be specified here, which is evaluated by the respective plugin. This should be described in the plugin documentation.
cmpConfiguration
If the plugin does not prevent it, it is possible to set configuration parameters directly on the plugin component via a cmpConfiguration object.
This can be useful, for example, if the plugin does not have its own title, but the hook displays the plugins as tabs.
{
"cmpConfiguration": {
"title": "TAB1",
"iconCls": "x-fa fa-fire"
}
}|
An incorrect/inappropriate configuration can lead to errors when creating or using the plugin. |
hookSubId
Some modules use the same hook multiple times. In this case, a hookSubId may be used for differentiation. If this is the case, the appropriate hookSubId must also be set here in the JSON configuration.
If a hookSubId is configured here, the hook must also have this hookSubId. Otherwise, the plugin will not be displayed.
The use of hookSubId should be displayed in the documentation of the respective hook.
{
"hookSubId": "passende_hookSubId_zum_hook"
}