Keycloak as an identity provider
Keycloakfootnote: [Keycloak is a trademark of The Linux Foundation] is an "Open Source Identity and Access Management" that can be used as an identity provider (IdP) for user authentication and authorization.
The following describes how to configure the BPC with Keycloak as an identity provider.
Prerequisite
You have installed Keycloak and have administrative access to Keycloak and BPC.
|
You should always use the latest version of Keycloak to avoid security risks. |
Configuration Keycloak
Please create a realm for the BPC or use an existing realm that you may already be using for other applications.
|
It is not recommended to use the realm |
A script that configures the following points via API can be found in the section Script for automatic setup.
Create client
A client must be created so that the BPC can communicate with the Keycloak.
-
Make sure that you have selected the correct realm.
-
Select "Clients" on the left-hand side
-
Create a new client via "Create client"
-
Select "OpenID Connect" as "Client type"
-
Assign a client ID, e.g.
bpc.
This must later match the configurationclient_idin the BPC. -
Activate "Client authentication". In older Keycloak versions, this corresponds to the access type "confidential".
-
Enter the URL of your BPC under "Valid redirect URIs". E.g. "https://bpc.example.com/"
-
Save the client
-
You can view (and change) the client secret in the "Passwords" (or "Credentials") tab.
This must later match the configurationclient_secretin the BPC.
Create BPC roles
To be able to appoint BPC administrators, you need the role bpcadmin.
-
Select "Realm roles" on the left-hand side
-
Create the role
bpcadminvia "Create role".
Create or assign BPC administrator
For a user to be an administrator in the BPC, they need the role bpcadmin.
-
Select "User" on the left-hand side
-
Create a new user via "Add user" or select an existing user
-
Assign the role
bpcadminto the user
Configure role mappings
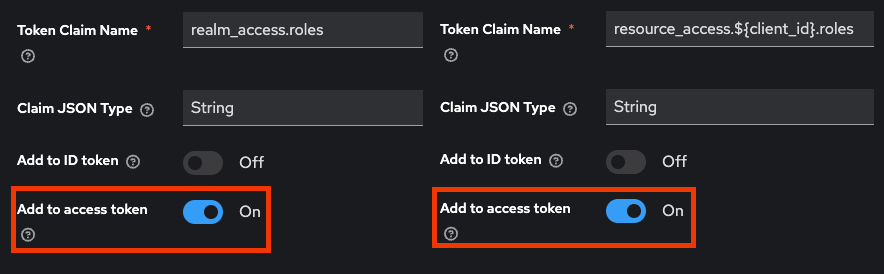
In order for the BPC to successfully recognize the roles and the Identity Management API can be used (necessary for user administration in the frontend), the option "Add to access token" must be activated for the role client scopes.
This should be set automatically when a new realm is created.
If it is not set, navigate in the Keycloak administration page in the BPC realm to Client-Scopes→roles→Mappers and activate the option for both mappers "realm roles" and "client roles".
Configuration BPC
In the BPC, Keycloak must be created as an identity provider at Backend Connections and then defined as the identity provider to be used in the Core Services settings.
|
When the BPC is started, backend Connections are automatically created that can be used for the Keycloak.
These contain a suitable placeholder configuration and have the names |
Identity Provider Keycloak vs. OIDC
You have the option of connecting Keycloak in two different variants (IdentityProvider OpenID Connect (OIDC) or Keycloak).
In both variants, the actual authentication takes place via the OpenID Connect protocol.
In the pure OpenID Connect (OIDC) variant, user administration takes place exclusively in Keycloak.
If you select "Keycloak", the User administration / Identity Manager integrated in the BPC can be used.
Keycloak-specific configuration of the Backend Connection
Specific configurations for Keycloak Backend Connections are described below.
For the general configuration of Backend Connections of type identity_provider see General Identity Provider Configuration.
| Setting (Key) | Group | Example value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
config |
|
Set Keycloak or OIDC for the Backend Connection as IdP. |
|
IdentityProvider_ |
oidc |
|
OIDC Discovery Endpoint. |
IdentityProvider_ |
oidc |
|
An diese Adresse wird der Benutzer weitergeleitet, nachdem ein Login ausgeführt wurde. |
IdentityProvider_ |
oidc |
|
An diese Adresse wird der Benutzer weitergeleitet, nachdem ein Logout ausgeführt wurde. |
IdentityProvider_ |
oidc |
|
Comma-separated list of all claim names from which the user’s roles are extracted. |
IdentityProvider_ |
oidc |
|
Comma-separated list of all claim names from which the user’s organizations are extracted. |
IdentityProvider_ |
oidc |
|
Comma-separated list of all claim names from which the user’s rights are extracted. |
oidc |
|
OIDC scopes that are requested from the OIDC provider during authentication. If scopes are requested that do not exist or for which the client is not authorized, errors may occur during authentication. |
|
IdentityProvider_ |
oidc |
|
ID of the client configured in the OIDC provider to be used for access. |
IdentityProvider_ |
oidc |
|
Secret for the authentication of the client access. |
oidc |
|
The PKCE method (Proof Key for Code Exchange) used for a hardened login flow. You can choose between |
|
API authentication via access tokens |
oidc |
|
Enables authentication at the API via access tokens issued by the OIDC provider. |
Check access token at the introspection endpoint |
oidc |
|
If activated, the access token is checked at the OIDC provider’s introspection endpoint. This can be used to check whether the session with the OIDC provider has ended. Otherwise, only the signature of the token is validated, which is sufficient in most cases if a token is valid for a short time. |
BPC integration
If you have selected the type Keycloak in the setting identityProvider, various integrations are available.
The BPC provides access to various user administration functions via the integrated user administration.
The user account menu plugin can also be used to execute various actions against the keycloak by the user.
Script for automatic setup
For development and test environments, the following script can be used to configure a Keycloak so that it can be used with BPC.
This script uses the Admin REST API of Keycloak and sets up a new realm bpc. This is then configured so that it can be used with BPC.
This is then configured so that it works with the preconfigured identity provider Keycloak (ID: idp_keycloak).
|
The script can be used, for example, if you temporarily start a Keycloak via Docker for testing. |
The variables of the script should be adjusted as required.
However, it is not necessary to set ADMIN_USER and ADMIN_PASSWORD.
These two variables are queried via the terminal at startup.
createBpcRealm.sh#!/bin/bash
# Keycloak Server URL und Admin Credentials
KEYCLOAK_URL="http://localhost:8080"
KEYCLOAK_REALM="master"
ADMIN_USER=""
ADMIN_PASSWORD=""
# Neue Realm-, Client- und Benutzer-Konfiguration
NEW_REALM="bpc"
NEW_CLIENT="bpc"
CLIENT_SECRET="bpc-test-only"
NEW_ROLE="bpcadmin"
BPC_USER="bpcuser"
BPC_ADMIN="bpcadmin"
# Benutzer-Daten
BPC_USER_FIRSTNAME="BPC"
BPC_USER_LASTNAME="User"
BPC_USER_EMAIL="bpcuser@example.com"
BPC_ADMIN_FIRSTNAME="BPC"
BPC_ADMIN_LASTNAME="Admin"
BPC_ADMIN_EMAIL="bpcadmin@example.com"
# Redirect-URL für den Client
REDIRECT_URL="http://localhost*"
# Funktion zur Eingabe von Benutzername und Passwort
read -p "Gib den Keycloak Admin Benutzernamen ein: " ADMIN_USER
read -s -p "Gib das Keycloak Admin Passwort ein: " ADMIN_PASSWORD
echo ""
# Abrufen eines Tokens vom Keycloak-Server
TOKEN=$(curl -s \
-d "client_id=admin-cli" \
-d "username=$ADMIN_USER" \
-d "password=$ADMIN_PASSWORD" \
-d "grant_type=password" \
"${KEYCLOAK_URL}/realms/${KEYCLOAK_REALM}/protocol/openid-connect/token" | jq -r .access_token)
# Prüfen, ob das Token erfolgreich abgerufen wurde
if [ -z "$TOKEN" ]; then
echo "Fehler beim Abrufen des Tokens. Überprüfe Benutzername/Passwort und Keycloak-URL."
exit 1
fi
# Realm "bpc" erstellen mit Internationalisierung
# Für Login Theme die folgende Zeile mit aufnehmen
# "loginTheme": "theme-id",
echo "Erstelle den Realm '${NEW_REALM}' mit Login-Theme 'foo-theme' und Internationalisierung..."
curl -s -X POST "${KEYCLOAK_URL}/admin/realms" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"realm": "'"${NEW_REALM}"'",
"enabled": true,
"internationalizationEnabled": true,
"supportedLocales": ["en", "de"],
"defaultLocale": "en"
}'
# Client "bpc" erstellen
echo "Erstelle den Client '${NEW_CLIENT}' im Realm '${NEW_REALM}' mit Redirect-URL '${REDIRECT_URL}'..."
curl -s -X POST "${KEYCLOAK_URL}/admin/realms/${NEW_REALM}/clients" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"clientId": "'"${NEW_CLIENT}"'",
"secret": "'"${CLIENT_SECRET}"'",
"enabled": true,
"redirectUris": ["'"${REDIRECT_URL}"'"],
"directAccessGrantsEnabled": true
}'
# Realm-Rolle "bpcadmin" erstellen
echo "Erstelle die Realm-Rolle '${NEW_ROLE}'..."
curl -s -X POST "${KEYCLOAK_URL}/admin/realms/${NEW_REALM}/roles" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"name": "'"${NEW_ROLE}"'"
}'
# Benutzer "bpcuser" erstellen
echo "Erstelle den Benutzer '${BPC_USER}'..."
curl -s -X POST "${KEYCLOAK_URL}/admin/realms/${NEW_REALM}/users" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"username": "'"${BPC_USER}"'",
"firstName": "'"${BPC_USER_FIRSTNAME}"'",
"lastName": "'"${BPC_USER_LASTNAME}"'",
"email": "'"${BPC_USER_EMAIL}"'",
"enabled": true,
"credentials": [{
"type": "password",
"value": "'"${BPC_USER}"'",
"temporary": false
}]
}'
# Benutzer "bpcadmin" erstellen
echo "Erstelle den Benutzer '${BPC_ADMIN}'..."
curl -s -X POST "${KEYCLOAK_URL}/admin/realms/${NEW_REALM}/users" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"username": "'"${BPC_ADMIN}"'",
"firstName": "'"${BPC_ADMIN_FIRSTNAME}"'",
"lastName": "'"${BPC_ADMIN_LASTNAME}"'",
"email": "'"${BPC_ADMIN_EMAIL}"'",
"enabled": true,
"credentials": [{
"type": "password",
"value": "'"${BPC_ADMIN}"'",
"temporary": false
}]
}'
# Benutzer-ID des Benutzers "bpcadmin" abrufen
BPC_ADMIN_ID=$(curl -s -X GET "${KEYCLOAK_URL}/admin/realms/${NEW_REALM}/users?username=${BPC_ADMIN}" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" | jq -r '.[0].id')
# Rollen-ID der Rolle "bpcadmin" abrufen
ROLE_ID=$(curl -s -X GET "${KEYCLOAK_URL}/admin/realms/${NEW_REALM}/roles/${NEW_ROLE}" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" | jq -r '.id')
# Rolle "bpcadmin" dem Benutzer "bpcadmin" zuweisen
echo "Weise die Rolle '${NEW_ROLE}' dem Benutzer '${BPC_ADMIN}' zu..."
curl -s -X POST "${KEYCLOAK_URL}/admin/realms/${NEW_REALM}/users/${BPC_ADMIN_ID}/role-mappings/realm" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '[
{
"id": "'"${ROLE_ID}"'",
"name": "'"${NEW_ROLE}"'"
}
]'
# Abrufen der Scope-ID für "profile" im Realm "bpc"
echo "Rufe die Scope-ID für 'profile' im Realm '${NEW_REALM}' ab..."
PROFILE_SCOPE_ID=$(curl -s -X GET "${KEYCLOAK_URL}/admin/realms/${NEW_REALM}/client-scopes" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" | jq -r '.[] | select(.name == "profile") | .id')
# Prüfen, ob die Scope-ID für "profile" gefunden wurde
if [ -z "$PROFILE_SCOPE_ID" ]; then
echo "Fehler: Der Scope 'profile' wurde im Realm '${NEW_REALM}' nicht gefunden."
exit 1
fi
# Mapper "Impersonator User ID" zum "profile" Scope hinzufügen
echo "Füge dem Scope 'profile' den Mapper 'Impersonator User ID' hinzu..."
curl -s -X POST "${KEYCLOAK_URL}/admin/realms/${NEW_REALM}/client-scopes/${PROFILE_SCOPE_ID}/protocol-mappers/models" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"name": "Impersonator User ID",
"protocol": "openid-connect",
"protocolMapper": "oidc-usersessionmodel-note-mapper",
"config": {
"user.session.note": "IMPERSONATOR_ID",
"id.token.claim": "true",
"introspection.token.claim": "true",
"access.token.claim": "true",
"claim.name": "impersonator.id",
"jsonType.label": "String"
}
}'
# Mapper "Impersonator Username" zum "profile" Scope hinzufügen
echo "Füge dem Scope 'profile' den Mapper 'Impersonator Username' hinzu..."
curl -s -X POST "${KEYCLOAK_URL}/admin/realms/${NEW_REALM}/client-scopes/${PROFILE_SCOPE_ID}/protocol-mappers/models" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"name": "Impersonator Username",
"protocol": "openid-connect",
"protocolMapper": "oidc-usersessionmodel-note-mapper",
"config": {
"user.session.note": "IMPERSONATOR_USERNAME",
"id.token.claim": "true",
"introspection.token.claim": "true",
"access.token.claim": "true",
"claim.name": "impersonator.username",
"jsonType.label": "String"
}
}'
echo "Fertig!"|
Execution of the script is at your own risk. No guarantee is given for the function. An insecure secret is set for the client in the script. This should never be used in productive environments. |
Provide Keycloak health checks
Keycloak offers a management interface with health checks.
The health check endpoints are available if the environment variable KC_HEALTH_ENABLED is set to the value true.
The management interface is typically provided on the Port 9000; the health endpoints are /health/live, /health/ready, /health/started and /health.
If you want to set up the Docker container with the health check endpoints as described in the section Script for automatic setup, you must specify the arguments -p 9000:9000 and -e KC_HEALTH_ENABLED=true.
After setting up, you can set the health check URL (e.g. http://localhost:9000/health/ready) and query it via the status API as described in Configuring the identity provider.
