Templates
Templates are always linked to organizations, whereby a data management component corresponds to an organization.
The Assets are derived from the templates.
There are several ways to create a template for data management.
|
Note that requests are case-sensitive. |
General structure of templates
<api>
<organizationId>organizationID</organizationId>
<locale>en</locale>
<requests>
<request>
<module>am</module>
<context>template</context>
<method>create/update/delete</method>
<parameters>
<template>
<customId>Selbstgewählte ID</customId>
<id>ID</id>
<labels>
<de>Template-Name auf Deutsch</de>
</labels>
<versionedAttributes>
<attribute>... </attribute>
<attribute>... </attribute>
</versionedAttributes>
<unversionedAttributes>
<attribute>... </attribute>
</unversionedAttributes>
<use> Zugriffsverwaltung </use>
<parents> ... </parents>
<children> ... </children>
</template>
</parameters>
</request>
</requests>
</api>For more information on the organizationId.
Depending on the selected method, the respective elements customId, id and use optional.
Structure
| Element | Description | Example | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
An identifier that is generated when the template is created.
It is required (as an alternative to
|
|
||
|
An identifier that can be set manually.
It is required (as an alternative to To change the char values only → no number values → combination works (Id-33) → best to name the same as template label → without Labels or display is used for both by CustomID |
|
||
|
The XPATH used to evaluate the final HTML color code for display in the frontend. The defined XPATH can be used to evaluate the versioned attributes or the time series data based on the keywords defined in the XPATH. The permitted "keywords" are: “/asset/versionedAttributes”. |
|
||
|
Contains language-specific designations/labels of the template. |
|
||
These attributes use historization, so that when they are updated, the new values do not replace the current values, but are added to the database.
The last version is only marked as obsolete, so that it remains in the database. |
|
|||
These attributes do not use historization, so when they are updated, the new values replace the current values. |
|
|||
|
Fields of the assets/master data. |
|
||
|
List of templates that can be children of the current template. |
|
||
|
List of templates that can be parents of the current template. |
|
||
|
Actions can be defined for a template, e.g. a plant can be switched off or a service task can be triggered. |
Examples
Example structure of a "create" template for products in the "Supermarket" organization
<api>
<organizationId>supermarkt</organizationId>
<locale>de</locale>
<requests>
<request>
<module>am</module>
<context>template</context>
<method>create</method>
<parameters>
<template>
<customId>Produkt</customId>
<versionedAttributes>
<attribute>
<key>Anfangsproduktnummer</key>
<type>number</type>
<required>true</required>
<unique>true</unique>
</attribute>
<attribute>
<key>Produkt</key>
<type>group</type>
<attributes>
<attribute>
<key>Produktart</key>
<type>string</type>
<required>true</required>
<enums>
<enum>
<key>1</key>
<labels>
<de>Lebensmittel</de>
</labels>
</enum>
<enum>
<key>2</key>
<labels>
<de>Süßwaren</de>
</labels>
</enum>
<enum>
<key>3</key>
<labels>
<de>Drogerieartikel</de>
</labels>
</enum>
<enum>
<key>4</key>
<labels>
<de>Getränke</de>
</labels>
</enum>
</enums>
</attribute>
<attribute>
<key>Herkunftsland</key>
<type>string</type>
<required>true</required>
</attribute>
</attributes>
</attribute>
<attribute>
<key>Produktname</key>
<type>string</type>
<required>true</required>
<unique>true</unique>
</attribute>
<attribute>
<key>Lagerort</key>
<type>group</type>
<attributes>
<attribute>
<key>Lager</key>
<required>true</required>
<type>enum</type>
<enums>
<enum>
<key>1</key>
<labels>
<de>Hochregallager</de>
</labels>
</enum>
<enum>
<key>2</key>
<labels>
<de>Kühlhaus</de>
</labels>
</enum>
</enums>
</attribute>
<attribute>
<key>Lagerort</key>
<type>group</type>
<required>true</required>
<attributes>
<attribute>
<key>regal-nr</key>
<labels>
<de>Regal Nummer</de>
</labels>
<type>number</type>
</attribute>
<attribute>
<key>regalbrett</key>
<labels>
<de>Regalbrett-Platz</de>
</labels>
<type>string</type>
</attribute>
</attributes>
</attribute>
</attributes>
</attribute>
<attribute>
<key>Herkunftsland</key>
<type>string</type>
<required>true</required>
</attribute>
<attribute>
<key>Kommentar</key>
<type>string</type>
<required>false</required>
<multiline>true</multiline>
</attribute>
</versionedAttributes>
<unversionedAttributes/>
</template>
</parameters>
</request>
</requests>
</api>Example structure of a "create" template for stores in the "Supermarket" organization
<api>
<organizationId>supermarkt</organizationId>
<locale>de</locale>
<requests>
<request>
<module>am</module>
<context>template</context>
<method>create</method>
<parameters>
<template>
<customId>Filiale</customId>
<descriptionAttribute>
<hidden>true</hidden>
</descriptionAttribute>
<versionedAttributes>
<attribute>
<key>Filialleitung</key>
<type>string</type>
<required>true</required>
<defaultValue>Max Mustermann</defaultValue>
</attribute>
<attribute>
<key>Adresse</key>
<type>group</type>
<collapsed>false</collapsed>
<attributes>
<attribute>
<key>Straße</key>
<type>string</type>
<required>true</required>
<defaultValue>Muster Straße</defaultValue>
<minLength>5</minLength>
</attribute>
<attribute>
<key>Hausnummer</key>
<type>string</type>
<required>true</required>
<defaultValue>42</defaultValue>
</attribute>
<attribute>
<key>plz</key>
<type>string</type>
<minLength>5</minLength>
<maxLength>5</maxLength>
<required>true</required>
<defaultValue>12345</defaultValue>
</attribute>
</attributes>
</attribute>
</versionedAttributes>
<unversionedAttributes/>
<children>
<template>
<id>55</id>
<minimumQuantity>0</minimumQuantity>
<maximumQuantity>0</maximumQuantity>
<customId>Produkt</customId>
<displayName>Produkt</displayName>
</template>
</children>
</template>
</parameters>
</request>
</requests>
</api>Attribute properties
The following attribute properties can be used for both Attributes with history and Attributes without history.
| Property | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
Primary key that identifies an attribute. |
|
|
Title or name of the attribute. |
|
|
Predefined selection of options |
|
|
Displayed name for the field, otherwise automatically inserted by the Labels. |
|
|
||
|
Description of attributes |
|
|
Data type of the attribute, see Data types of an attribute |
|
|
Enables the entry of several lines in a pop-up window |
|
|
The user cannot edit the value manually. This is only a hint for the default frontend and does not restrict access via the API |
|
|
The user cannot edit the value manually. This is only a hint for the default frontend and does not restrict access via the API. |
|
|
This value is used if no value is available (e.g. during creation). |
|
|
An attribute can have a color code. |
|
|
Value is not displayed in the standard frontend. |
|
|
Unique value |
|
|
Decides whether the group is displayed open or closed by default. |
|
|
Minimum value for numbers |
|
|
Maximum value for numbers |
|
|
Minimum length for strings |
|
|
Maximum length for strings |
|
Fields marked with * must be defined.
Examples
Example for attribute "enum"
<attribute>
<required>true</required>
<key>Produktart</key>
<type>enum</type>
<displayName>Produktart</displayName>
<enums>
<enum>
<key>lebensmittel</key>
<displayName>Lebensmittel</displayName>
<labels>
<de>Lebensmittel</de>
</labels>
</enum>
<enum>
<key>sueßwaren</key>
<displayName>Süßwaren</displayName>
<labels>
<de>Süßwaren</de>
</labels>
</enum>
<enum>
<key>drogerieartikel</key>
<displayName>Drogerieartikel</displayName>
<labels>
<de>Drogerieartikel</de>
<en>Drugstore items</en>
</labels>
</enum>
<enum>
<key>getraenke</key>
<displayName>Getränke</displayName>
<labels>
<de>Getränke</de>
</labels>
</enum>
</enums>
</attribute>Example for attribute "type"
<attribute>
<multiline>true</multiline>
<key>comment</key>
<type>string</type>
<displayName>Kommentar</displayName>
</attribute>Example for attribute "colorCode"
<colorCode>
<xpath>if (/asset/unversionedAttributes/attribute[key/text() = 'status']/value/text() = 'STATUS_OK') then '00ff00' else 'ff0000'</xpath>
</colorCode>
<unversionedAttributes>
<attribute>
<key>status</key>
<displayName>Status of Asset</displayName>
<value>STATUS_OK</value>
</attribute>
<attribute>
<key>meter_reading</key>
<displayName>Meter Reading</displayName>
<value>123</value>
</attribute>
</unversionedAttributes>Example of group of attributes
<attribute>
<required>true</required>
<key>Stellplatz</key>
<type>group</type>
<displayName>Stellplatz</displayName>
<attributes>
<attribute>
<labels>
<de>Regal Nummer</de>
</labels>
<key>regal-nr</key>
<type>number</type>
<displayName>Regal Nummer</displayName>
</attribute>
<attribute>
<labels>
<de>Regalbrett-Platz</de>
</labels>
<key>regalbrett</key>
<type>string</type>
<displayName>Regalbrett-Platz</displayName>
</attribute>
</attributes>
</attribute>Data types of an attribute
You can specify the type of a versioned and non-versioned attribute in the definition of the attribute.
The default type is "string".
User-defined attributes are always of type "string" with max. 1024 characters.
A data type "basic" can also be used for lists and table columns.
Data types "complex" cannot be nested, e.g. for lists or table columns. They also cannot contain groups.
| Class | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
basic |
boolean |
true/false |
number |
||
string |
||
password |
Simple password (not secret, just not displayed in the frontend). |
|
date |
No time zone allowed. Example: 2014-05-30 |
|
time |
No time zone allowed. Example: 23:59:59 |
|
dateTime |
No time zone allowed. Example: 23:59:59 |
|
enum |
Selection between specified options. |
|
dynamicEnum |
||
complex |
list |
Can contain attributes of the "basic" class type. |
table |
Can contain attributes of the "basic" class type. |
|
group |
group |
Can contain attributes of any type (basic, complex and group). |
Relationships between templates
When linking templates, there is a parent-child relationship.
If a template is a child of another template, this must be stored in the parent template under "children" and the parent template in the child under "parents".
The respective template must know about the relationship.
You can store multiple children and parents.
If no value is stored under "maximumQuantity", "0" is set and interpreted as "unlimited".
You can store either the CustomID or ID.
<children>
<template>
<id>53</id>
<minimumQuantity>0</minimumQuantity>
</template>
</children>- image
<parents>
<template>
<customId>Filiale</customId>
<maximumQuantity>1</maximumQuantity>
<displayName>Heimat</displayName>
</template>
</parents>For the effects in the interface view, see also Relationships between objects.
Create template
Via API call
Creating via API call is particularly suitable if several or numerous templates are to be created. numerous templates are to be created.
Prerequisites
-
HTTP or REST client (e.g. soapUI)
-
HTTP Request:
-
URI:
<schema>://<host>:<port>/ibis/rest/rc/am/protocoladapted to your specific installation -
HTTP Method: POST
-
Authentication: HTTP Basic Authentication
-
Login name, password: Login name and password of the user created here
-
Authorization Type: Set to "Preemptive" in soapUI
-
Request Body:
<request> <context><!-- e. g. asset, person, template --></context> <method><!-- e. g. create, get, query, update --></method> <module>am</module> <parameters> <!-- ... --> </parameters> </request>
-
See also Data Management API.
Create initial template
For an initial empty template, send the following request to Data Management using the HTTP/rest client:
<request>
<context>template</context>
<method>create</method>
<module>am</module>
<parameters>
<return>true</return>
</parameters>
</request>
The Parameters return, which is set to "true", instructs Data Management to return the newly created template.
The technical ID of the newly created template is always returned.
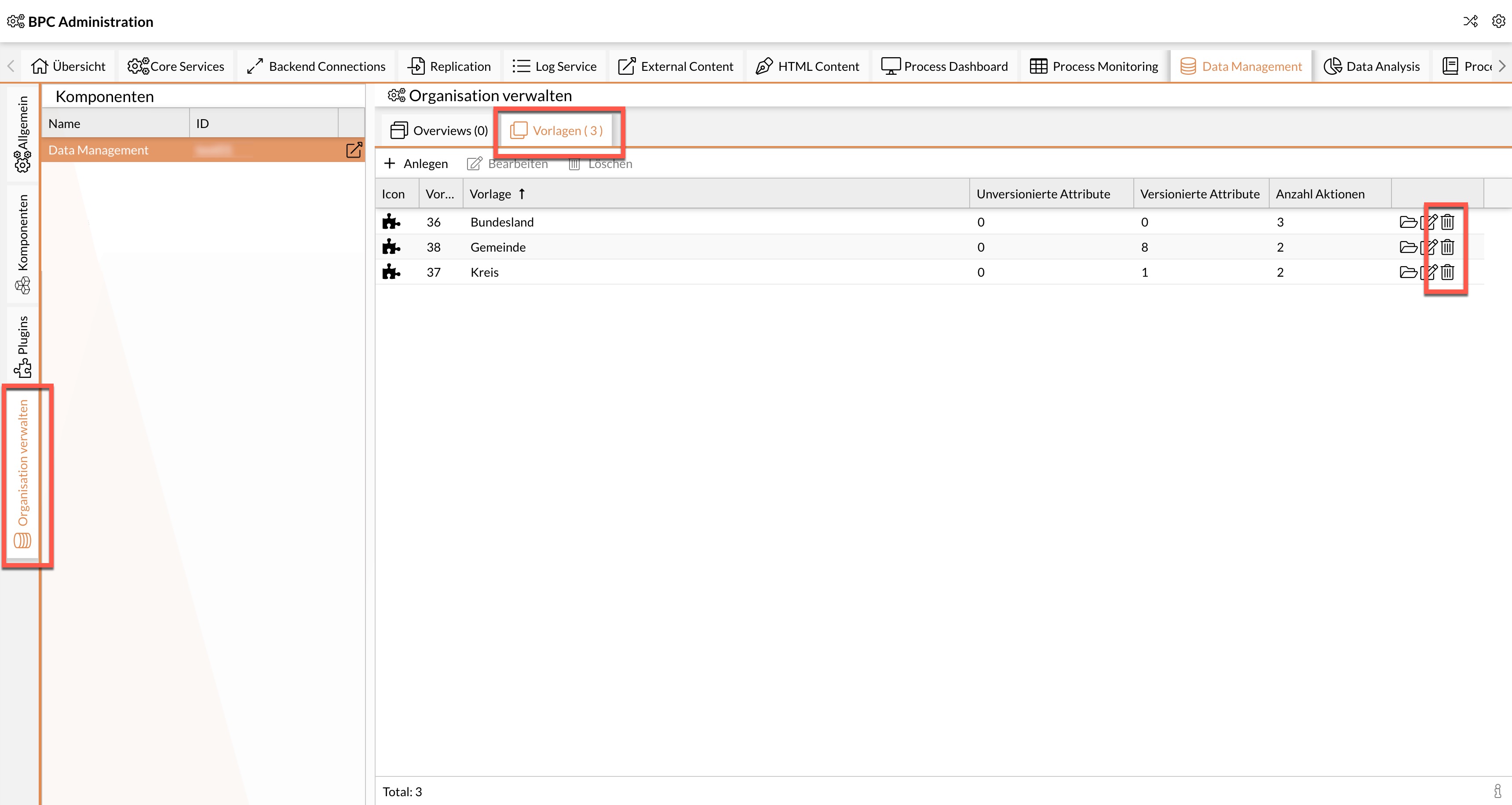
Via template editor in BPC
The creation via template editor is more suitable for individual templates, as the module components are created and configured individually by hand.
-
Open the "Data Management" tab in the BPC administration area.
-
Select the module component created during installation.
-
Select the "Manage organization" tab.
-
Select the "Templates" tab.
-
Create a new template.
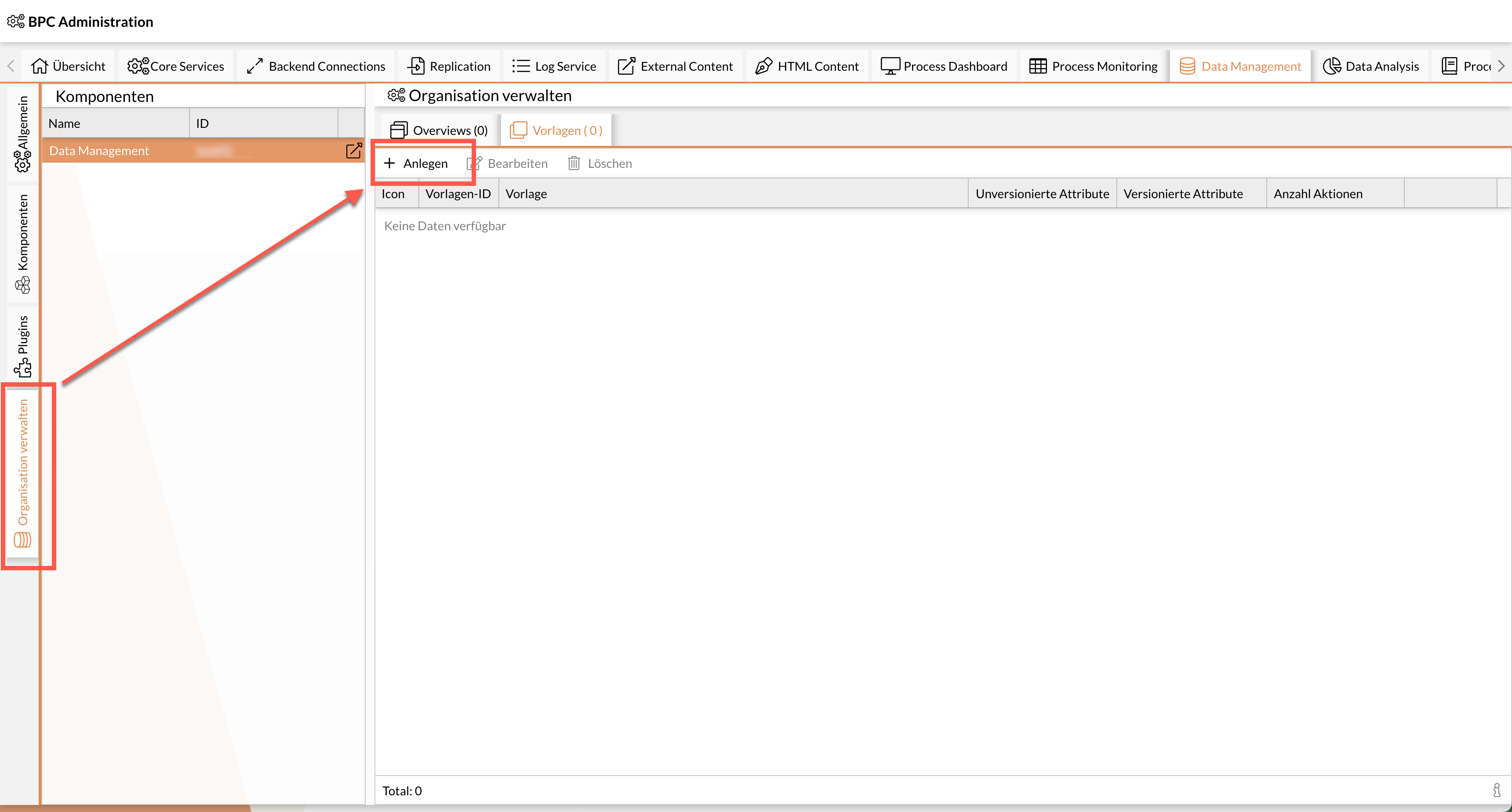
-
Write/copy the XML structure of the template into the editor.
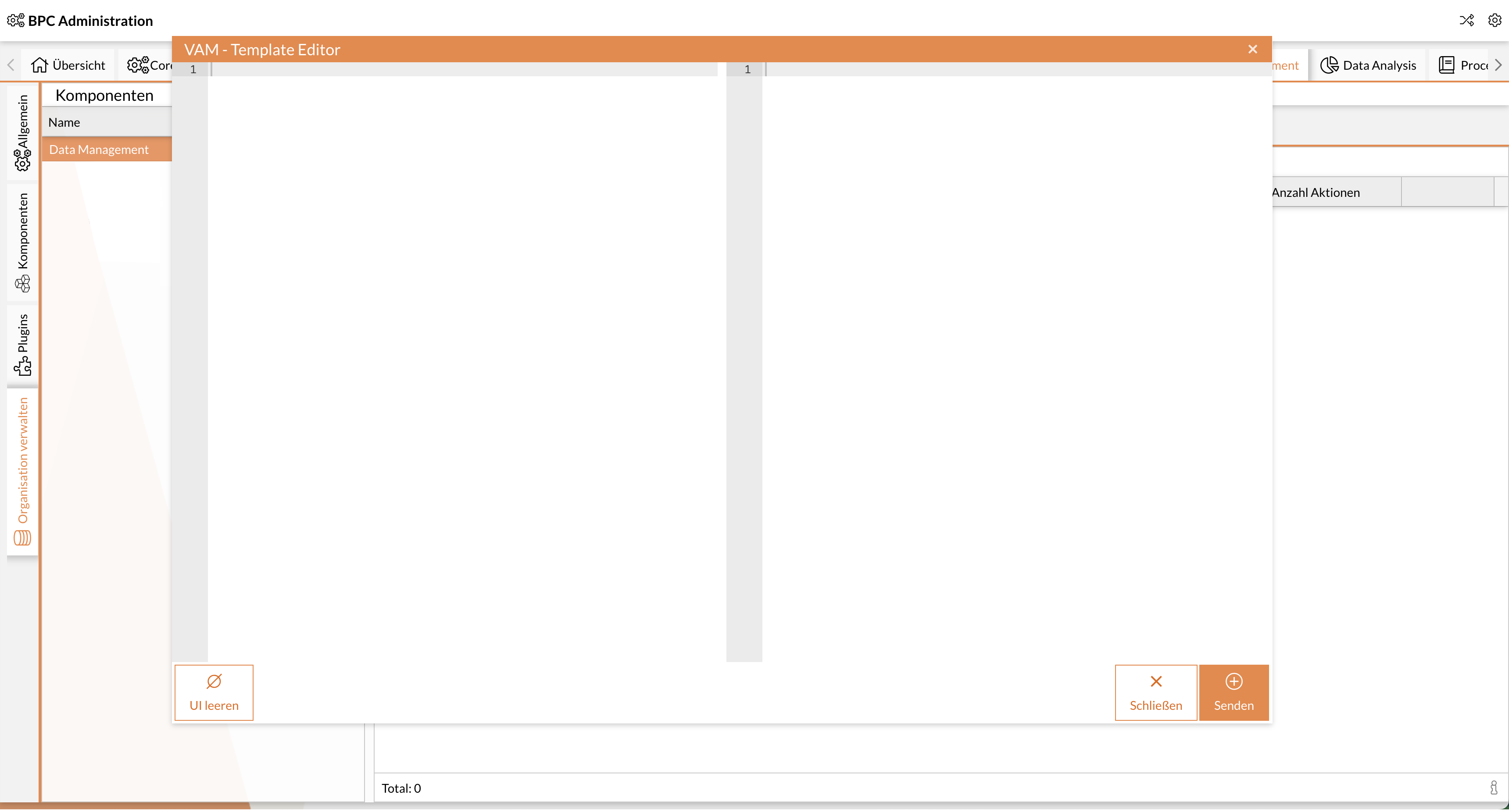
Example see General structure of templates.
Update template
|
Last update applies
If changes are made in the BPC interface of the Data Management module, these changes become visible in the module. |
Via API call
See xref:data_management:admin/api_calls.adoc
|
It is not possible to edit templates in the same way as assets.
If templates are changed via API call, the entire template must first be requested and then the desired element must be changed. |
Using the template editor in the BPC
Existing templates can be customized in the BPC interface.
-
Open the "Data Management" tab in the BPC administration area.
-
Select the desired module component.
-
Select the "Manage organization" tab.
-
Select the "Templates" tab.
-
Call up the desired template for editing.
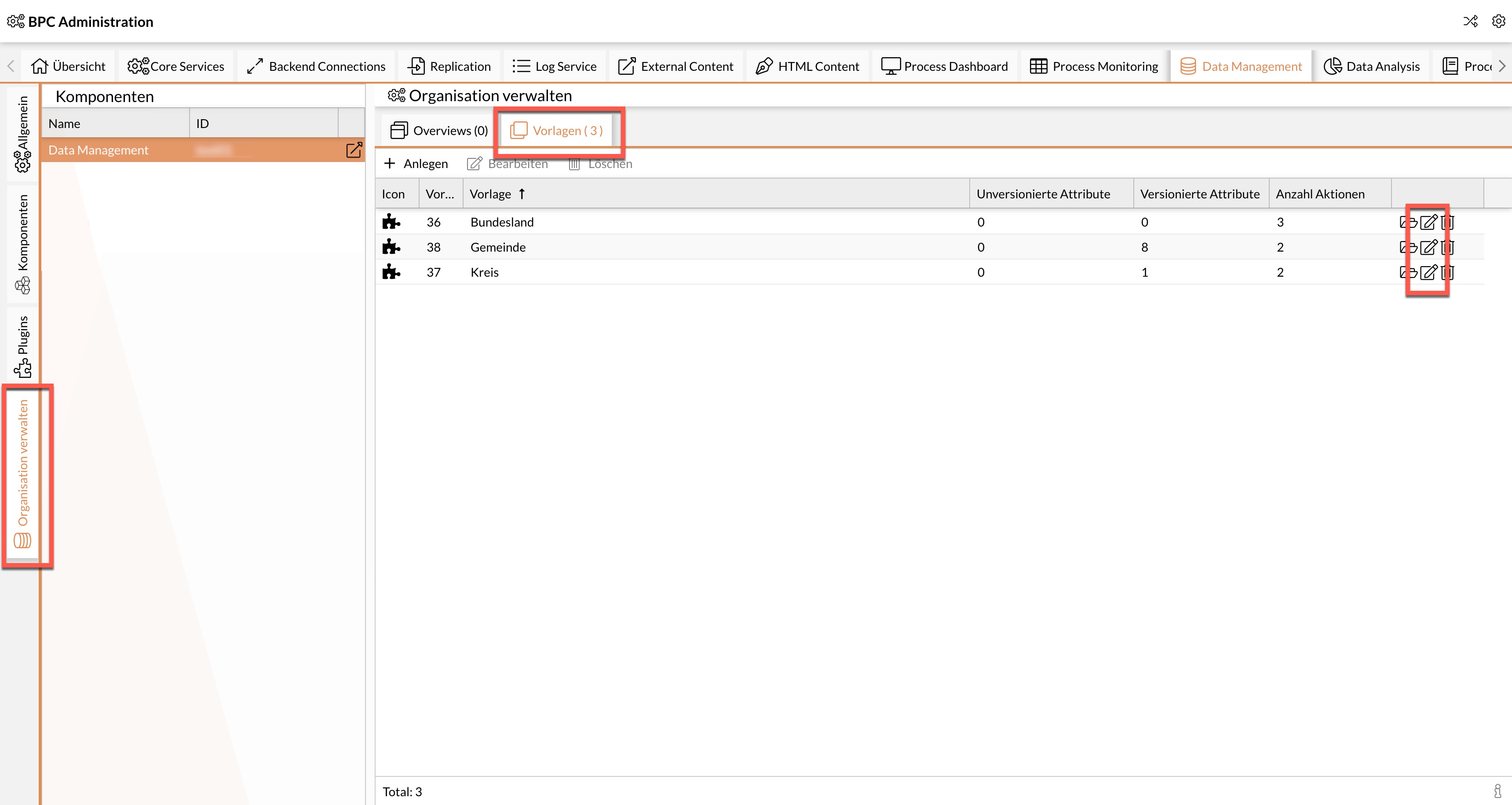
-
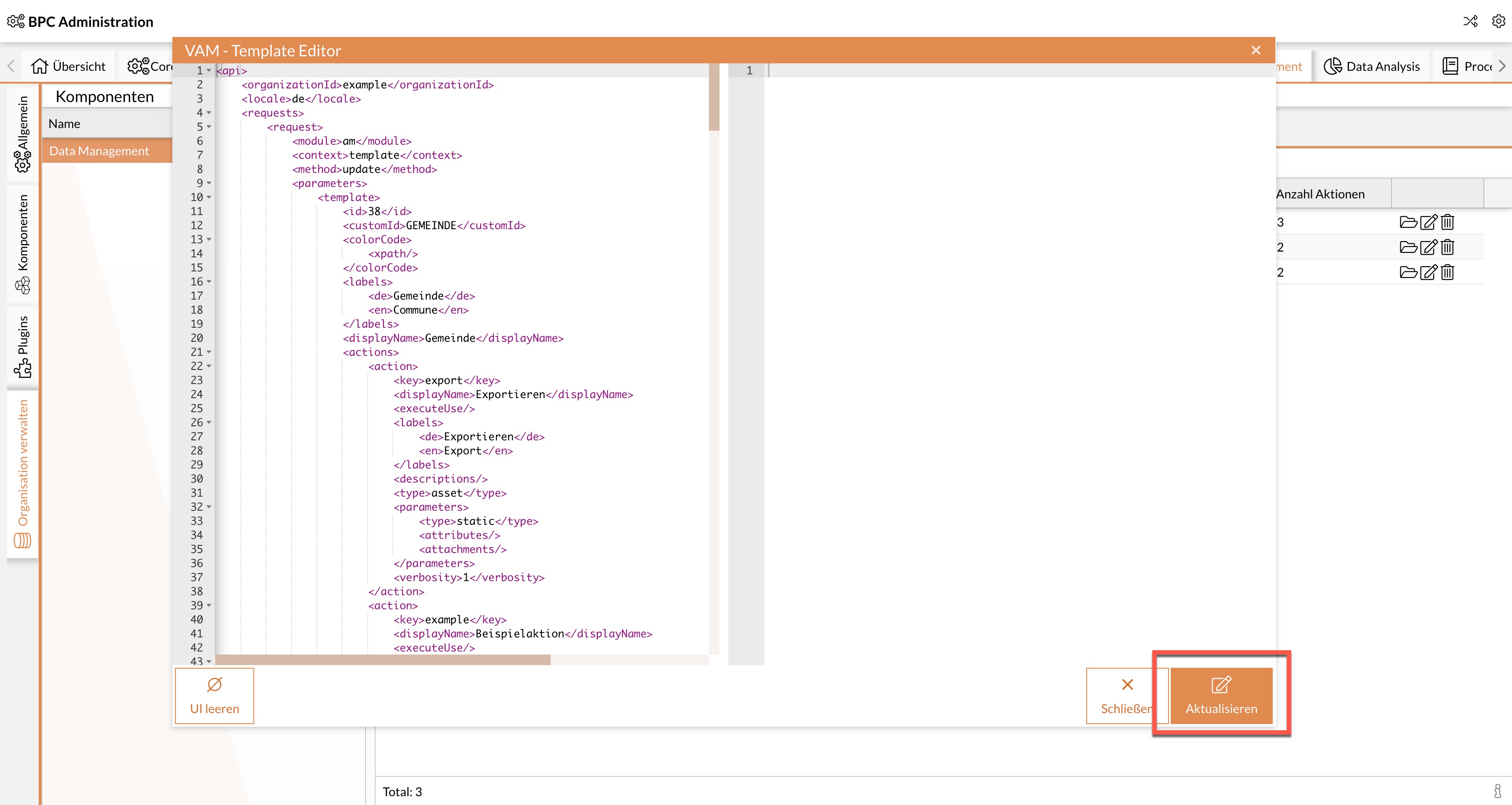
Make the desired adjustments in the template editor.
-
Select Update.
Delete template
Before deleting a template, all master data objects created with the template must be deleted. There must therefore no longer be any dependencies.
If templates are deleted via the BPC interface, they are tagged in the database and are therefore no longer displayed in the interface. However, they are still stored in the database.
-
Open the "Data Management" tab in the BPC administration area.
-
Select the desired module component.
-
Select the "Manage organization" tab.
-
Select the "Templates" tab.
-
Delete the desired template.
To permanently delete from the database:
-
Permanently delete all deleted elements of the template
-
DELETE FROM TEM_LABELS WHERE TEMPLATEID = $ID; -
DELETE FROM TEM_CHILDREN WHERE TEMPLATEID = $ID; -
DELETE FROM TEM_PARENTS WHERE TEMPLATEID = $ID;
-
-
DELETE FROM TEMPLATES WHERE ID = $ID;
