Backend Connections
The various configuration options for the Backend Connections are presented and described below.
Creating a Backend Connection
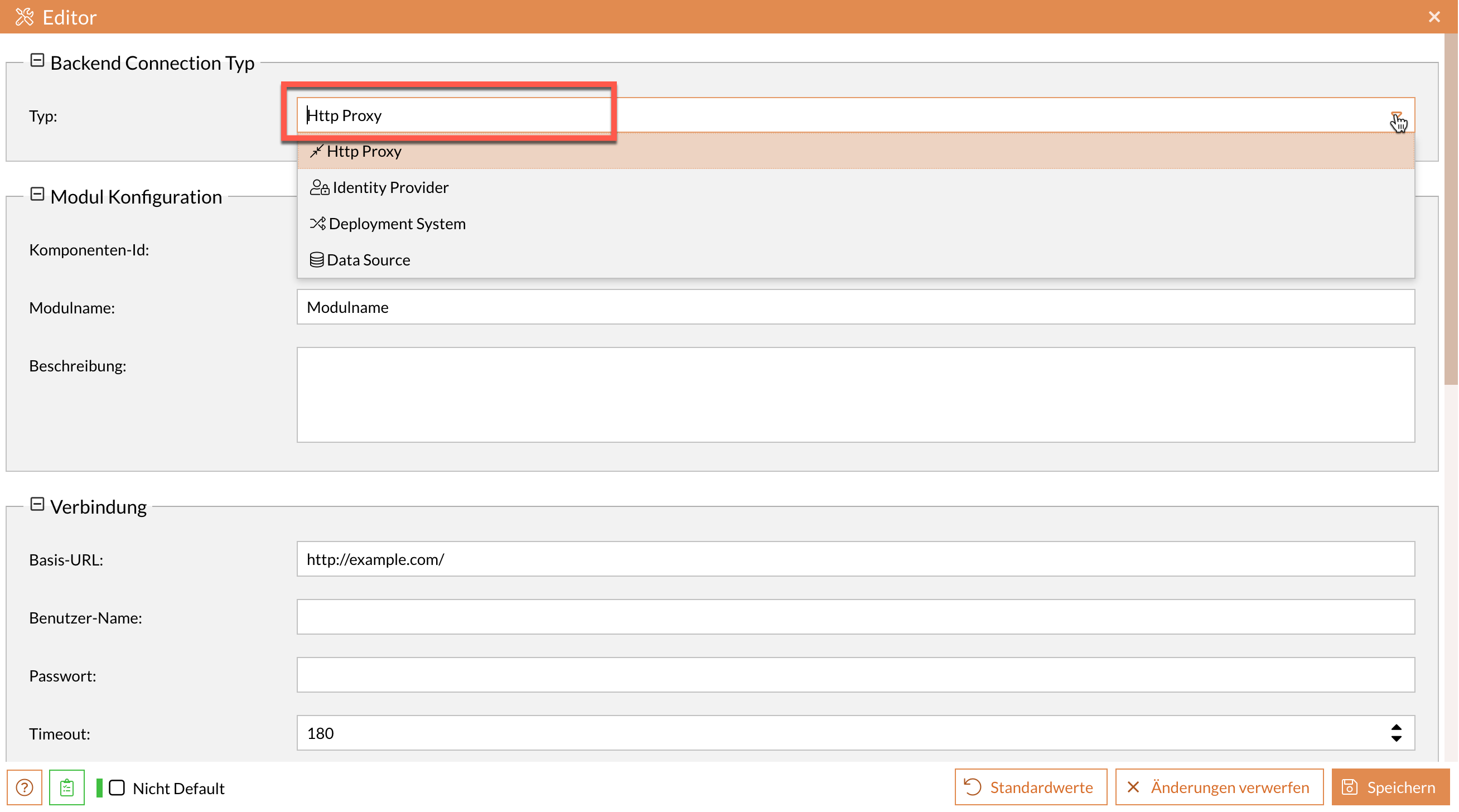
Add a new component in the Backend Connections tab.
The type of Backend Connection is selected using the "Type" input field. The specific configuration options are displayed depending on the type selected.
Help tools are available for initial and subsequent editing of the individual fields and settings.
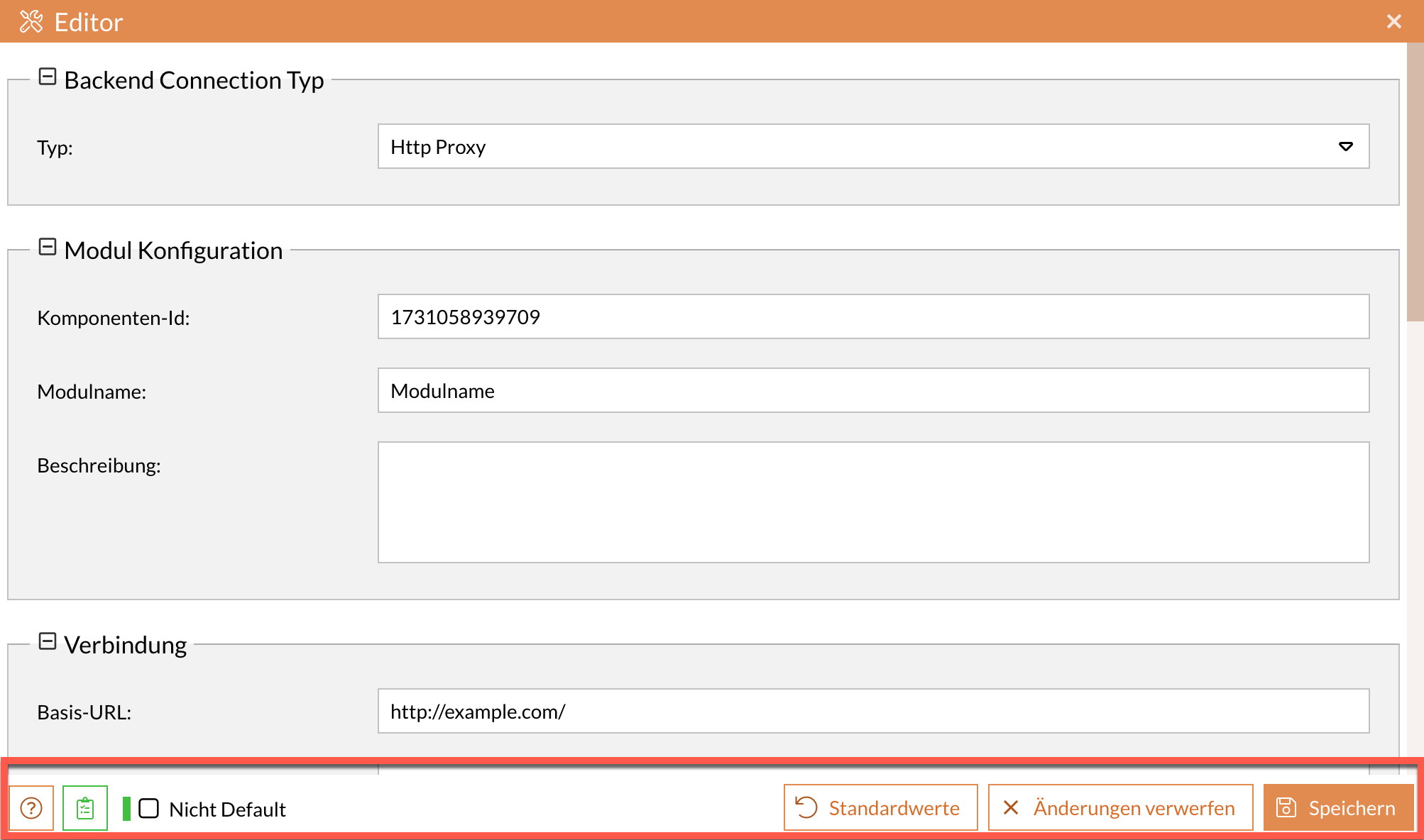
-
Shows or hides help texts. -
Validates the code of the relevant fields and displays the number of any errors and a corresponding error message. -
Not default
When this function is activated, only the settings that deviate from the default value are displayed. -
Default values
Resets all fields and settings to the default values. -
Discard changes
Resets all values to the last memory status.
When a new Backend Connection is created, the values are therefore reset to the default state. -
Save
Saves the new Backend Connection with all possible entries and settings. This component then appears in the component overview below the corresponding group.
General module configuration
These are the configuration parameters that are available for all Backend Connections.
| Setting (Key) | Group | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
ModuleHeader |
Module |
bool |
Enables the ModuleHeader to be deactivated/activated |
Module_Description |
Module |
text |
Enables a short description of the module to be stored. Can be displayed in the ModuleHeader, for example. |
Module_Icon |
Module |
text |
Displayed FontAwesome icon of the Backend Connection instance. |
Module_Name |
Module |
text |
Name of the module |
Connection types
There are various connection types, which are described below.
http_proxy
This enables the setup of an internal proxy for HTTP connections through the BPC. This enables, for example, access via External Content module component to a server that requires a login via BasicAuth or is not directly accessible, but only via proxy.
| Setting (Key) | Group | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Connection_Password |
Module |
text |
Password for authentication of the Connection (BasicAuth on the target server) |
Connection_Username |
Connection |
text |
Username for authentication of the Connection |
Connection_Timeout |
Connection |
number |
Maximum timeout of the Connection. |
Security |
bool |
Enables the deactivation/activation of the CSRF token check. |
|
Connection_SendSessionId |
Security |
bool |
If active, a session ID (in the header |
Connection_InjectUserSessionJWT |
Security |
bool |
The OIDC ID token is set in the header ( |
Connection_UntrustedCertificates |
Security |
text |
All certificates are trusted and the Common Name (CN) check is skipped. |
Http_Header_Filter |
Proxy |
json |
List of header names that are to be filtered out.
For security reasons, the BPC API key header ( Default: |
ProxyServer_Port |
Proxy |
number |
The Port under which the proxy server can be reached. |
ProxyServer_URL |
Proxy |
text |
The address of the proxy server to be used. Remains empty if a direct connection to the target server is possible. |
Target_BaseURL |
Target |
text |
This parameter defines the base URL to the target system and is prefixed each time it is used. |
The BPC session cookie is filtered for each forwarded call via an HTTP proxy so that a recipient cannot use the BPC in the context of the user.
If it is necessary to check the identity and validity of the user on the recipient side, this is possible via the options sendSessionId or injectUserSessionJWT.
In the case of sendSessionId, the user’s session ID is also sent via the header X-Bpc-SessionId.
The session can then be checked via the GET endpoint /cxf/bpc-core/authentication/session/{sessionid} (see Authentication API).
In the case of injectUserSessionJWT, the ID token of the Open-ID-Connect provider is also sent in the header X-Bpc-Session. The signature must be signed with the public key.
The signature must be validated with the public key of the OIDC provider.
If you also need to check authorisations through roles, rights and organisations, it is necessary to configure the OIDC provider so that these are included in the ID token.
identity_provider
This connection type enables the configuration of the identity provider used.
The exact configuration parameters are described under Configuration of the identity providers.
deployment_system
This connection type enables the configuration of the BPC systems that are to be addressed as source and target at Deployment.
| Setting (Key) | Group | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
DeploymentSystem_SortPriority |
Config |
number |
Adjustment of the sort order (selection box in the Deployment dialog). Default: 1000 |
DeploymentSystem_URL+
( |
Target |
text |
Base URL to the target system and is prefixed each time it is used. |
DeploymentSystem_AllowUntrustedConnections |
Connection |
bool |
Allow untrusted connections. |
DeploymentSystem_ApiKey |
Connection |
text |
API Key of the target system |
data_source
This connection type is used for the configuration of database connections. For these connections it is necessary that the appropriate database driver is installed beforehand.
| Setting (Key) | Group | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
DataSource_Configuration |
Datasource |
json |
Additional data source configuration options that are not covered by the general (DataSource_User, …) are covered. Default: |
DataSource_DriverName |
Datasource |
text/combobox |
Database drivers such as oracle, mysql, mariadb |
DataSource_Password |
Datasource |
text |
Password of the database user |
DataSource_URL |
Datasource |
text |
JDBC Connection URL to the database. |
DataSource_User |
Datasource |
text |
Name of the database user |
|
In most cases, only a read-only connection is required for the connection to the database. To prevent security problems, it is recommended to use a database user with read-only rights in accordance with the least privilege principle. |
DataSource_Configuration
The "DataSource_Configuration" configuration parameter is mainly used to configure the pool used with the data connections. A data source holds a pool with n connections to the database. The individual replication jobs each retrieve such a connection and return it to the pool once the work is done. The size should therefore be selected sensibly. Setting this value too high (>8 or >16) is not necessarily advantageous or can even lead to errors if, for example, the Oracle database does not allow so many simultaneous connections (= ask DB Admin for the appropriate number). Further pool settings can be found HERE.
| Setting | Type | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
pool |
String |
dbcp2 |
the pool to be used |
xa |
String |
true |
as XA resource. Activates the option for distributed transactionshttps://docs.oracle.com/cd/E13218_01/wlp/docs81/sp2/db/5XA.html[(JDBC XA]). The recommended setting here is true. |
pool.minIdle |
String |
2 |
The minimum number of connections that can remain idle in the pool, without extra ones being created, or zero to create none. |
pool.maxIdle |
String |
5 |
The maximum number of connections that can remain idle in the pool, without extra ones being released, or negative for no limit. |
pool.maxTotal |
String |
10 |
Max. number of database Connections in the pool. Max. number of database connections in the pool |
If Closed Connection errors occur repeatedly with Oracle, include the following settings.
| Setting | Type | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
pool.testOnBorrow |
String |
true |
Validation of the DB connection on removal from the pool. |
pool.testOnReturn |
String |
true |
Validation of the DB connection when returning to the pool. |
factory.validationQuery |
String |
select 1 from dual |
SQL query that returns exactly one hit.
This is used to test the connection. |
factory.validationQueryTimeout |
String |
15 |
Execution timeout in seconds for the defined validation query. |
{
"pool.testOnBorrow": "true",
"pool.testOnReturn": "true",
"factory.validationQuery": "select 1 from dual",
"factory.validationQueryTimeout": "15"
}Documentation on the Parameters: BasicDataSource Configuration Parameters
|
|
file_storage
This connection type is used to configure connections to cloud storage providers. For these connections, it is necessary that the corresponding file storage modules for connecting to the cloud services are installed beforehand.
AWS S3 (incl. API-compatible Services such as MinIO), Azure Blob Storage (incl. API-compatible Services) and Google Cloud Storage are supported.
The type of cloud storage provider is set via the setting fileStorageType.
You can choose from s3, azureBlobStorage and googleCloudStorage.
Depending on the provider, the following settings must be configured. It must be ensured that the accesses have read, write and delete rights via access keys (AWS S3), account keys (Azure Blob Storage) or service accounts (Google Cloud Storage).
In addition, the following setting can be used to control whether downloads take place directly via the cloud storage service or are routed via the BPC.
| Setting (Key) | Group | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Endpoint URL |
config |
bool |
Routes files via the BPC. Activate this option if direct links to cloud storage are blocked by firewalls. |
|
Changing and deleting File Storage Backend Connections can cause existing downloads and uploads to be aborted. This can happen, for example, if rolling access keys are exchanged in the connection. |
AWS S3
| Setting (Key) | Group | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Endpoint URL |
config |
String |
The full URL of the S3-compatible storage endpoint. Can be left blank for AWS S3 connections. |
Region |
config |
String |
The region of the S3 service (e.g. us-east-1). For S3-compatible providers, leave empty if necessary (default 'us-east-1') or enter a user-defined value. |
Access-Key |
config |
String |
The access key for authentication with the S3 service. Corresponds to the user ID for access. |
Secret-Key |
config |
String |
The secret key for the access key. Is required for secure authentication. |
Azure Blob Storage
| Setting (Key) | Group | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Endpoint URL |
config |
String |
The full URL of the Azure Service. (e.g. |
Account name |
config |
String |
The Azure account name. (e.g. |
Account-Key |
config |
String |
The account key to access the Azure Blob Storage. |
Google Cloud Storage
| Setting (Key) | Group | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Project-ID |
config |
String |
The Project-ID of the Google Cloud Account. |
Service-Account |
config |
Json |
The Service-Account JSON content. The Service account requires read, write and delete permissions on the Google Cloud storage. |
