Data Management Access management
This page describes organizations, roles and rights that provide access to various data and functions of this module.
For more information, see Authentication and authorization in the BPC.
|
Organizations, roles and rights are not case-sensitive.
For example, the BPC does not differentiate between |
For a user to be able to use this module, they first need the right loadModule_vam.
See also loadModule_MODULE_ID
The loadModule_backendconnection permission is also required for both module admins and module users.
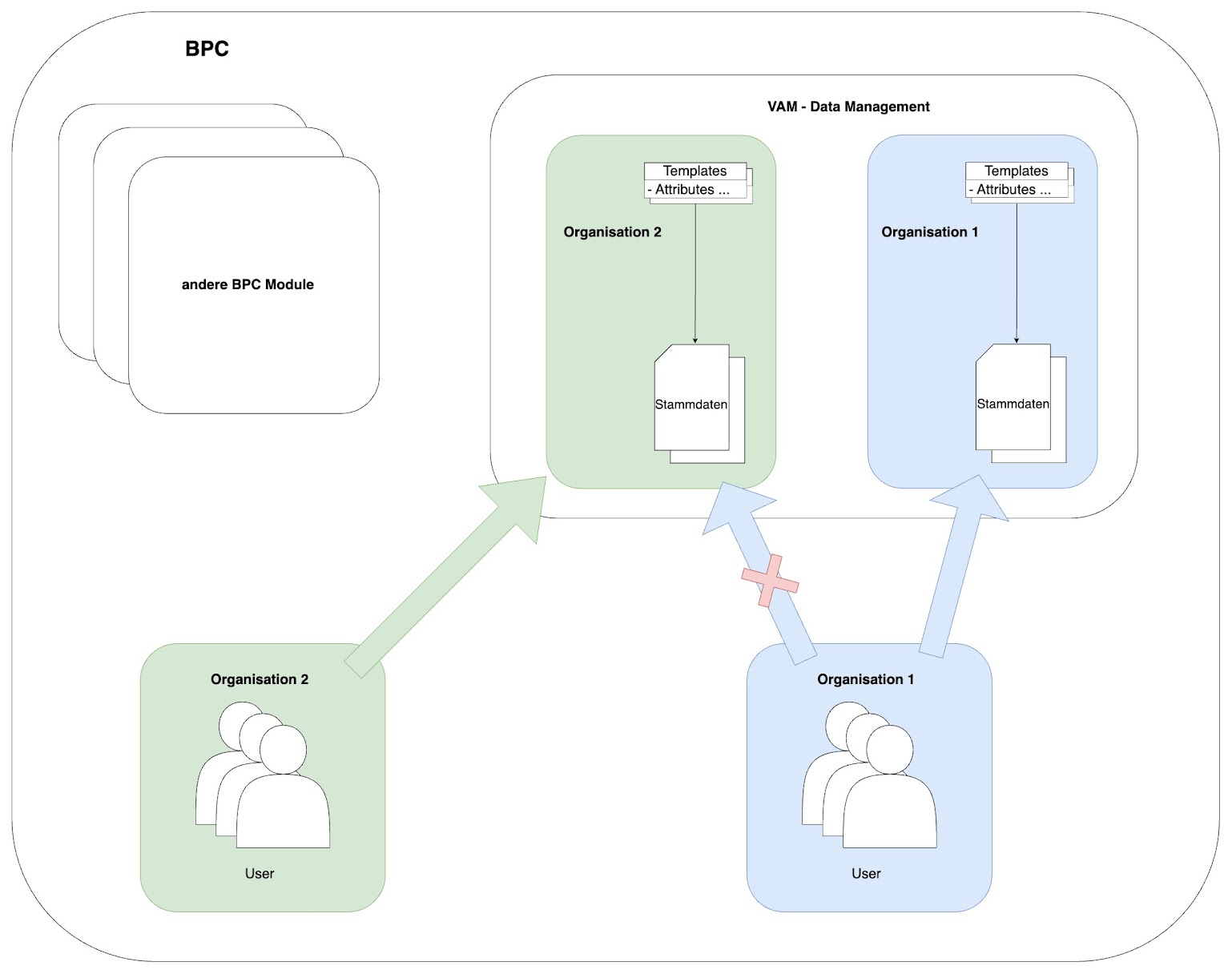
Organization
If a user is a member of an organization in BPC, they have access to this organization in Data Management.
The organization is the functional and technical environment within which templates and assets are assigned and stored. The OrganizationID in particular defines the storage location in which templates and assets are stored and can be found in a bundle.
Roles and rights
- VAM_organization_$ID
-
Role defined in the template for read/write access to the template of the specified ID and all derived templates.
Alternative to assignment to the organization ID in the BPC.
- VAM administrator
-
Universal administrator for all organizations, templates and assets in Data Management.
|
The "VAM administrator" role cannot make any configurations in the BPC "Data Management" module.
"bpcadmin" is required to make changes to the entire Data Management module. |
Templates
For templates, the respective rights and roles must be defined on the template itself at use.
The right must be filled with corresponding roles.
The definition of use on the template is saved unchanged (short forms are not resolved).
There is an additional computedUse for this - "write" and "any" are resolved here and all additional implied roles are included.
Possible rights at use:
-
read
Open and view templates/assets -
create
Create templates/assets, implies automaticread -
update
Edit templates/assets, implies automaticread -
delete
Delete templates/assets, implies automaticread -
write
Union ofcreate,updateanddelete -
executeAction
Perform actions in templates/assets, implies automaticread -
any
Union ofwriteandexecuteActionor Union of all conceivable authorizations
Example:
<use>
<read>
<role>DM_reader</role>
</read>
<write>
<role>DM_writer</role>
</write>
</use>
Actions
For actions, the rights/roles for the respective action must be defined via executeUse.
At least one role is required.
Application examples and fallback solutions
-
Grant permissions for "all"
-
Give all users the "VAM administrator" role
Problem: does not allow two different VAM organizations to be treated differently -
Use "bpcuser" role
Every BPC user has this role and can therefore be used if something should be allowed for everyone (provided they can call up the relevant organization at all).
-
-
Organization-specific permissions
Define an "any" role at the organization and give it to all potential users:<use> <any> <role>MCS-administrator</role> </any> </use> -
Some users should only be able to read
Define an "any" role at the organization or at the templates:<use> <read> <role>MCS-read</role> </read> <any> <role>MCS-administrator</role> </any> </use> -
Set the same permissions for all templates
useSet in the INUBIT in the configuration of the organization:Permissions defined there automatically apply to all templates - as if the roles had also been added individually at each location.
Actions
-
Enable certain roles for all actions
It is possible to define roles in the templateuse/executeActionso that these roles apply to all actions of this template.
|
In this case, the template is also automatically visible for these roles, because the authorization |
-
Enable roles for all actions in all templates + set
use/executeActionin the organization configuration (INUBIT):
Example diagram
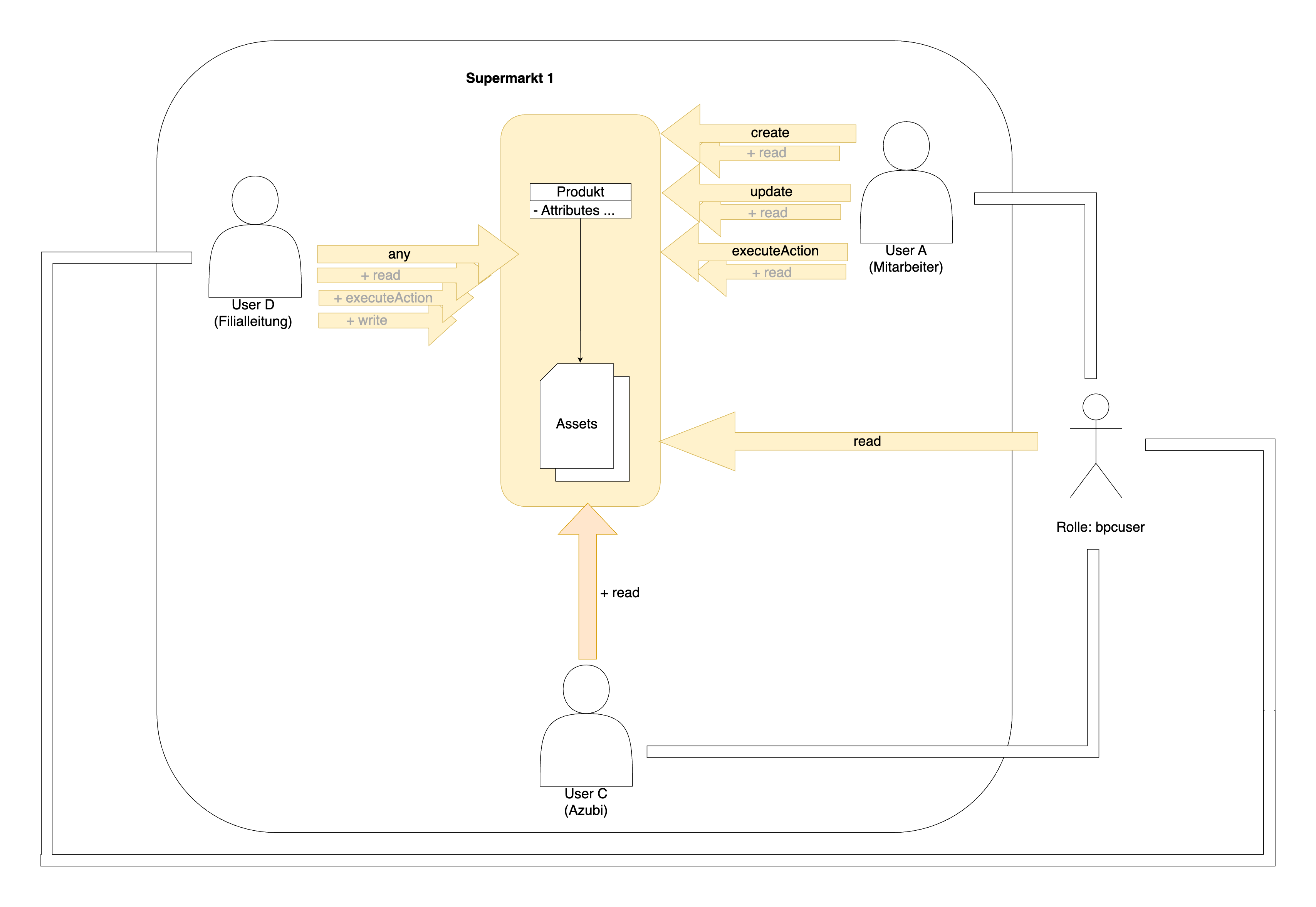
The following example explains the distribution of rights for the "Supermarket 1" organization.
Each user shown in the Diagram is part of the "Supermarket 1" organization.
User A, who represents an employee, is granted the rights create, update & executeAction to the template product.
With each of these rights, the user implicitly receives the read right read to the assets (master data objects) of the template.
The store manager, also called user D in this case, has been granted the right any for the template product.
All existing rights fall under this right.
This right is compiled in the background from the other rights read, executeAction & write.
The stick figure, which represents the role bpcuser, was stored in the product template for the read right read.
Every new user in the BPC automatically receives the role bpcuser when it is created, which is represented in this Diagram by the lines extending from the stick figure.
As every user has the role bpcuser, every user who is part of the organization "Supermarket 1" can now also read the master data objects of the template, as in this case user C, who represents an apprentice.
